Checking the calories in food before eating is another habit we all may have. Managing calorie intake and working on weight loss is good.
But what about basic nutrition? Our body needs good nutrition to function well and maintain good health. Not just that, good nutrition plays a key role in how successful the diet plan functions. Lack of adequate nutrition can result in poor energy and performance, chronic disease, or serious health problems.
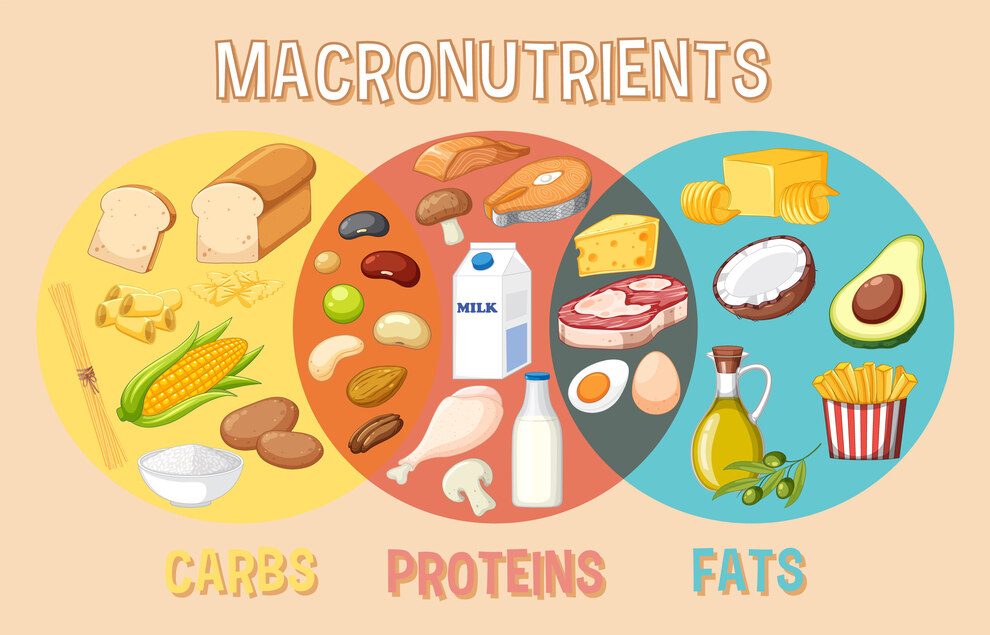
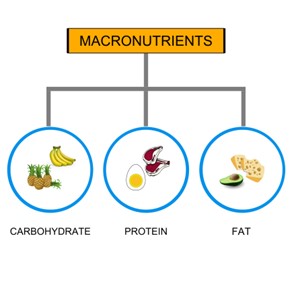
Getting good nutrition is essential for the healthy functioning of our body. These nutrients are classified into two categories, based on the amount required by our body. Macro-nutrients and Micro-nutrients.
Macro-nutrients
Macro-nutrients are important for the human body to grow healthy and function well. These are the elements of food which are required in large quantity for our body, which is why these is called macro-nutrients also known as “macros”.
Macro-nutrients are categorised by mainly three nutrients- carbohydrates, proteins and fats. We can get these macros from our diet itself, as our body cannot produce them by itself. Each macro-nutrient gives different amounts of calories to our body - 1gm of carbohydrate gives 4 calories, 1gm protein gives 4 calories and 1gm fat gives 9 calories. All three nutrients have different functions and tasks to perform in our body.
 Our body needs carbohydrates for quick energy. Carbohydrates are a favourite source of fuel for our body as it doesn’t take a lot of effort to get energy from carbs. These macro-nutrients are easily broken down by our body to get energy in the form of glucose (sugar) which is the same type of sugar found in our bloodstream. All the cells of our body need this glucose to function but our brain and muscles are the biggest users.
Our body needs carbohydrates for quick energy. Carbohydrates are a favourite source of fuel for our body as it doesn’t take a lot of effort to get energy from carbs. These macro-nutrients are easily broken down by our body to get energy in the form of glucose (sugar) which is the same type of sugar found in our bloodstream. All the cells of our body need this glucose to function but our brain and muscles are the biggest users.

Carbohydrates are a quick source of energy but they are not essential for survival as if our body does not get carbs for an extended period of time, it uses protein and fat as its source of energy. And this is how a ketogenic diet works.
Carbohydrates are subdivided into two categories, simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates are quick to break down into sugar because they are made up of highly processed and refined sugar and don’t contain any vitamins and minerals hence they are also called bad carbohydrates, whereas complex carbohydrates are processed more slowly and are full of various vitamins and minerals.
Sources of complex carbohydrates to include in your diet
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Sweet potatoes
- Legumes such as Lentils and chickpeas
- Whole wheat grains such as brown bread and pasta.

Proteins are not a direct source of energy, unlike carbohydrates. Proteins are all made up of amino acids. 1gm protein is made up of 22 amino acids, some are essentials that our body doesn’t produce by itself, some are partially essential and some are not essential, at all. Proteins play the role of building blocks for the structure of our body. The main function of this nutrient is to repair tissues and support the immune system. The quality of proteins is measured by the number of essential amino acids it contains. Meat, fish, eggs and milk products have all the amino acids and hence are considered good sources of complete protein. Soy protein is also a good source of protein, especially for vegetarians. The recommended daily intake of protein varies from person to person. For common people, it is nearly 0.75 to 1 gm per kilogram of body weight.
Sources of protein to include in your diet
- Fish
- Meat
- Eggs
- Seeds
- Nuts
- Legumes

Fats are the reserve energy for our body and it is also an important source of energy. Our body gets its energy in the form of glucose from the fats in the absence of carbohydrates. There are two types of fats, unsaturated fats and saturated fats. Unsaturated fat is good for our body as it regulates metabolism, maintains the elasticity of cell membranes, improves blood flow, and promotes cell growth and regeneration. Saturated fat is bad for our body as it provides cholesterol to our body. Our body produces cholesterol by itself, but introducing a small amount from food helps in hormone production like oestrogen and testosterone, the production of vitamin D. In contrast, cholesterol-rich diets can increase the risk of heart disease.
Sources of fat to include in your diet
- Avocado
- Diary
- Eggs
- Salmon fish
- Nuts
- Seeds
- Extra virgin olive oil
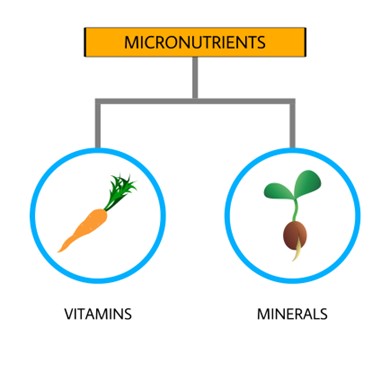
Micro-nutrients
Micro-nutrients are those elements of nutrients we need in smaller quantities like vitamins and minerals. We need vitamins and minerals in mg (milligrams) or mcg (micrograms). Like macro-nutrients, our body does not produce enough amount of micro-nutrients. Hence, we need to eat a diet rich in vitamins and minerals. These nutrients do not provide any calories but are equally important for the healthy function of our body. It helps in producing enzymes and hormones and acts as an antioxidant in your body. Each vitamin and mineral has a specific role in your body. Consuming a balanced diet, rich in all vitamins and minerals in adequate amounts helps you to fight against diseases.
Food sources high in Micro-Nutrients:
- Avocado
- Beans
- Nuts
- Lean beef
- Spinach
- Mushrooms
- Eggs
- Lentils
- Chicken
- Turkey
- Grains like oats, quinoa, brown rice
- Potatoes
- Salmon, tuna and seafood.